What Technology Goes into Autonomous Cars?
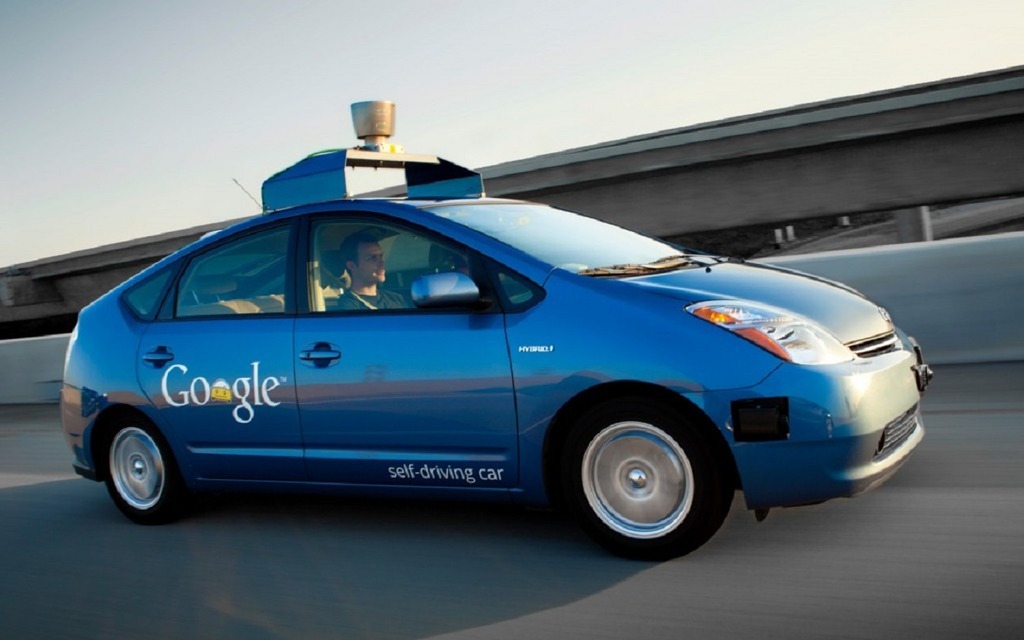
In the last century, several scientists who worked on driverless cars compared them to insects, as these are relatively simple organisms. They have organs that collect information—like antennae and eyes—as well as a brain to analyze the information received and a motor system to propel them.
In a car, sensors and cameras “see” what’s happening around the vehicle. Many of today’s models come with parking sensors or peripheral cameras, but the few autonomous cars that already exist have many more.
- Also: Easy Updates for Your Car
- Also: Urban Cruise Control
The “brain” of a car is its computer. Increasingly, new models are being equipped with electronic devices, but autonomous vehicles take it to the next level and often require two or three additional modules. It’s interesting to note that these components have benefitted tremendously by miniaturization. In 2010, the modules inside Google’s test vehicles were the same size as desktop computers, but these have been reduced to half the size in the past two years!
Lastly, the computer’s commands need to be converted into physical movement, and that’s where the motors come in. Motors are generally incorporated in the steering column (specifically on electric-assist steering systems, which are more popular nowadays) and they put the vehicle in motion. The accelerator doesn’t need to be moved; since it controls a computer, you just have to enter a command for the car to slow down or speed up.
- Is Canada Ready for Autonomous Vehicles?
- The First Autonomous Cars
- V2V Technology: The Future of Autonomous Vehicles